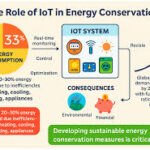
Weather App Development: Building a Real-Time Weather Application Using OpenWeatherMap API
Weather plays a critical role in our daily lives, influencing travel plans, work schedules, agriculture, logistics, and even health decisions. With the rise of smartphones and web applications, users now expect instant access to accurate weather information anytime and anywhere. This growing demand has made weather app development one of the most popular and practical projects in modern web development.
A weather app built using APIs like OpenWeatherMap provides real-time weather updates, short-term and long-term forecasts, and weather alerts for different locations around the world. Such applications are widely used in mobile apps, websites, smart devices, and dashboards.
In this blog, we will explore how to build a weather app using the OpenWeatherMap API, discuss its features, architecture, implementation approach, challenges, and future enhancements.
What is a Weather App?
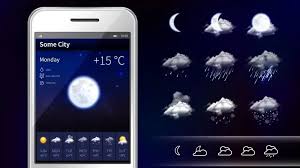
A weather app is a software application that fetches meteorological data from external APIs and displays it in a user-friendly format. It provides information such as:
- Current temperature
- Weather conditions (sunny, rainy, cloudy)
- Humidity and wind speed
- Hourly and daily forecasts
- Weather alerts and warnings
Modern weather apps rely heavily on third-party weather APIs to ensure accurate and up-to-date information.
Why Build a Weather App?
Weather app development is a valuable project for developers because it combines real-world utility with practical technical skills.
Key Benefits of Building a Weather App
- Learn API integration
- Understand asynchronous programming
- Improve frontend UI/UX skills
- Practice real-time data handling
- Build a strong portfolio project
- Create a useful application for users
For beginners and intermediate developers, a weather app is an ideal project to demonstrate real-world problem-solving skills.
Introduction to OpenWeatherMap API
OpenWeatherMap is one of the most popular weather data providers. It offers a wide range of APIs that provide global weather data in real time.
Key Features of OpenWeatherMap
- Real-time weather data
- Hourly and daily forecasts
- Historical weather data
- Weather alerts
- Global city coverage
- JSON-based API responses
OpenWeatherMap is widely used due to its reliability, scalability, and developer-friendly documentation.
Core Features of a Weather App
A modern weather app should include the following essential features:
1. Real-Time Weather Updates
The app fetches current weather data based on:
- User’s location (GPS)
- City name input
- Latitude and longitude coordinates
Displayed data typically includes:
- Temperature
- Weather condition
- Humidity
- Wind speed
- Feels-like temperature
Real-time updates ensure users always receive the latest weather information.
2. Weather Forecasts
Forecasting is one of the most valuable features of a weather app.
Types of Forecasts
- Hourly forecast (next 24–48 hours)
- Daily forecast (5 to 7 days)
Forecasts help users plan activities, travel, and events more effectively.
3. Weather Alerts and Warnings
Weather alerts notify users about:
- Storms
- Heavy rainfall
- Heatwaves
- Extreme weather conditions
Alerts improve safety by providing timely warnings and recommendations.
4. Location-Based Weather
Users can:
- Search weather by city name
- Use current location
- Save favorite locations
Location-based weather makes the app more personalized and convenient.
5. User-Friendly Interface
A good weather app focuses on:
- Clean and intuitive UI
- Visual weather icons
- Responsive design
- Fast loading speed
User experience plays a major role in app adoption and retention.
Technology Stack for Weather App Development
A weather app can be built using various technologies depending on platform requirements.
Frontend Technologies
- HTML for structure
- CSS for styling and responsiveness
- JavaScript for logic and API handling
- Frontend frameworks (React, Vue, or Angular)
Backend (Optional)
- Node.js for API proxy
- Express for server routing
API
- OpenWeatherMap API
For most basic weather apps, a frontend-only implementation is sufficient.
How a Weather App Works
The working of a weather app follows a simple flow:
- User enters a city name or allows location access
- App sends a request to the OpenWeatherMap API
- API returns weather data in JSON format
- App processes and displays data on the UI
- Data refreshes periodically for real-time updates
This architecture ensures efficiency and scalability.
API Integration in Weather App Development
API integration is the core of weather app functionality.
Steps Involved
- Create an OpenWeatherMap account
- Generate an API key
- Send HTTP requests using fetch or Axios
- Handle API responses
- Display data dynamically
Proper error handling ensures the app works smoothly even when data is unavailable.
Data Display and UI Design
Weather data should be displayed in a visually appealing way.
Best UI Practices
- Use weather icons for conditions
- Display temperature prominently
- Use cards or sections for forecasts
- Include background changes based on weather
- Ensure mobile responsiveness
Good design improves usability and user satisfaction.
Performance Optimization
Weather apps must be fast and efficient.
Optimization Techniques
- Cache API responses
- Minimize API calls
- Lazy load forecast data
- Optimize images and icons
- Reduce unnecessary DOM updates
Efficient performance leads to a better user experience.
Security and API Key Protection
API keys should be protected to prevent misuse.
Best Practices
- Store API keys securely
- Use environment variables
- Restrict API usage in dashboard
- Use backend proxy if required
Security ensures the app remains reliable and cost-effective.
Challenges in Weather App Development
Despite its simplicity, weather app development presents several challenges:
- API rate limits
- Inaccurate location detection
- Network connectivity issues
- Handling extreme weather data
- UI complexity for forecasts
Addressing these challenges requires proper planning and testing.
Use Cases of Weather Apps
Weather apps are widely used across various industries:
- Travel and tourism
- Agriculture and farming
- Logistics and transportation
- Event planning
- Health and fitness
- Smart home systems
Their versatility makes weather apps highly valuable.
Future Enhancements for Weather Apps
A basic weather app can be enhanced with advanced features:
- AI-based weather predictions
- Voice assistant integration
- Push notifications
- Weather-based recommendations
- Multi-language support
- Progressive Web App (PWA) support
Future-ready weather apps focus on personalization and intelligence.
SEO Considerations for Weather Apps
If your weather app has a web interface, SEO matters.
SEO Best Practices
- Fast page loading
- Mobile-first design
- Clean URLs
- Proper meta tags
- Structured data
- Accessibility compliance
SEO helps your weather app reach a broader audience.
Conclusion
Weather app development using APIs like OpenWeatherMap is a practical and impactful project that combines real-time data handling, API integration, and modern web development skills. By implementing features such as real-time weather updates, forecasts, and alerts, developers can create applications that are both useful and technically impressive.
Whether you are a beginner learning API integration, a student building a portfolio project, or a developer creating a production-ready application, building a weather app is an excellent way to gain hands-on experience with real-world data and modern web technologies.
As technology continues to evolve, weather apps will become smarter, more personalized, and deeply integrated into our daily digital lives.