Cloud Migration: Strategies, Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses need to remain agile, scalable, and competitive. One of the most powerful ways to achieve this is through cloud migration—moving data, applications, and IT resources from on-premises servers to cloud-based environments. While cloud migration offers many advantages, including cost savings, scalability, and enhanced collaboration, it is not without challenges. Understanding the strategies, benefits, and potential hurdles of cloud migration is essential for any organization planning a move to the cloud.
What Is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration is the process of transferring a company’s workloads—applications, data, IT resources—from traditional on-premises infrastructure to a cloud-based environment. This could include public cloud services, private clouds, or hybrid clouds.
Cloud migration is more than just moving files; it often requires rethinking application architecture, reconfiguring networks, and implementing security and compliance measures. Organizations migrate to the cloud to improve efficiency, reduce costs, gain access to advanced technologies like AI and analytics, and provide remote accessibility for employees.
Types of Cloud Migration Approaches
- Lift-and-Shift (Rehosting):
Applications are moved to the cloud with minimal changes. This is a faster approach but may not fully leverage cloud-native features. - Replatforming:
Minor adjustments are made to applications to optimize performance in the cloud while avoiding major code changes. - Refactoring (Re-architecting):
Applications are redesigned or rebuilt to fully utilize cloud-native services such as serverless computing or containerization. - Repurchasing:
Existing applications are replaced with cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. - Retire or Retain:
Outdated or redundant systems may be decommissioned or retained on-premises if migration is unnecessary.
The choice of strategy depends on business goals, application complexity, timeline, and budget.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
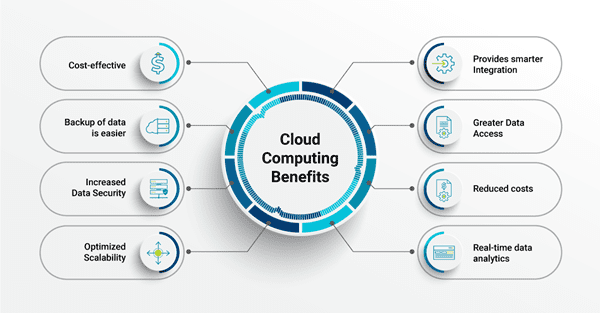
Cloud migration offers organizations significant benefits that extend beyond IT efficiency.
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most cited advantages of cloud migration is cost savings. Moving from expensive on-premises hardware to cloud-based services allows companies to pay only for what they use, avoiding unnecessary maintenance costs and capital expenditures.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud platforms provide on-demand scalability, enabling organizations to scale computing resources up or down based on business requirements. This ensures optimal performance during peak periods without over-provisioning resources.
3. Enhanced Security
Major cloud providers implement advanced security protocols, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular backups. Cloud migration also supports compliance with international standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, helping businesses protect sensitive data.
4. Improved Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud migration allows employees to access applications and data from anywhere, facilitating collaboration across remote and global teams. Cloud-based collaboration tools, such as Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, enhance productivity by enabling real-time document sharing and editing.
5. Innovation and Modernization
Migrating to the cloud unlocks access to advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, big data analytics, and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions. Organizations can innovate faster and respond more effectively to changing market conditions.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud migration often includes automated backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring critical data is protected and accessible even during unexpected outages or cyberattacks.
Cloud Migration Strategies
A structured approach is essential for successful cloud migration. Here are the most effective strategies:
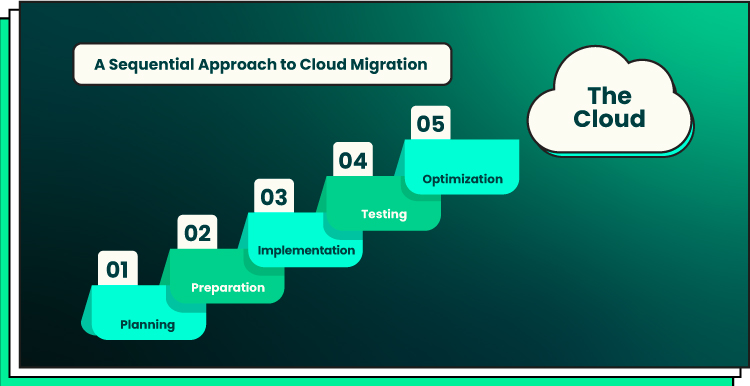
1. Assessment and Planning
Before migrating, organizations should evaluate existing IT infrastructure, applications, and workloads. Identify which systems are suitable for cloud migration and which require reconfiguration or replacement.
Key considerations include:
- Current and projected workload requirements
- Data sensitivity and compliance needs
- Application dependencies and integration requirements
- Cloud deployment model (public, private, or hybrid)
2. Selecting the Right Cloud Provider
Choosing a reliable cloud provider is critical. Evaluate providers based on security, compliance, pricing, support, and migration tools. Major options include:
- AWS: Comprehensive services with strong scalability
- Microsoft Azure: Integration with Microsoft products and enterprise solutions
- Google Cloud Platform: Strong AI and analytics capabilities
3. Phased Migration
Migrating workloads in phases reduces risk. Start with non-critical applications to test the process before moving core business systems.
4. Testing and Validation
Before fully switching over, test migrated workloads for performance, security, and compatibility. Validate integrations, data integrity, and application functionality.
5. Optimization Post-Migration
After migration, organizations should optimize resources for performance and cost efficiency. Monitoring tools and automated management systems can ensure workloads run efficiently and securely.
Challenges of Cloud Migration
Despite the advantages, cloud migration comes with challenges that must be addressed.
1. Downtime and Business Disruption
Migrating critical workloads can cause temporary downtime. To minimize impact, businesses must carefully plan migration windows, test procedures, and have fallback strategies in place.
2. Security and Compliance
Moving sensitive data to the cloud introduces security and compliance risks. Organizations must ensure proper encryption, access control, and compliance with legal requirements.
3. Cost Management
While cloud computing is cost-effective, poor management of cloud resources can lead to unexpected expenses. Regular monitoring and right-sizing resources are necessary to control costs.
4. Skill Gaps
Cloud migration requires specialized expertise. Companies may need to train staff or hire cloud professionals to manage and optimize the cloud environment.
5. Legacy Application Integration
Older applications may not be fully compatible with cloud environments. Refactoring or redesigning legacy systems can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Real-World Cloud Migration Examples
Netflix
Netflix migrated from on-premises data centers to AWS, enabling global streaming, automatic scaling, and high availability. This migration allowed Netflix to innovate faster and deliver content efficiently worldwide.
Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe transitioned its software from physical media to a cloud-based SaaS model. This shift improved accessibility for users and allowed Adobe to offer subscription-based pricing.
GE Healthcare
GE Healthcare migrated its medical imaging applications to the cloud to enable real-time collaboration among global healthcare teams, improve analytics, and ensure patient data security.
Best Practices for Cloud Migration
- Comprehensive Assessment: Evaluate workloads, dependencies, and cloud readiness.
- Security First: Include encryption, access control, and compliance in your plan.
- Phased Approach: Start with non-critical applications to reduce risk.
- Use Cloud Migration Tools: Utilize vendor-provided tools for smooth transfer and monitoring.
- Continuous Monitoring: Track resource usage, performance, and security post-migration.
- Training and Change Management: Prepare staff for new workflows and cloud technologies.
The Future of Cloud Migration
As businesses increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud environments, cloud migration will continue to evolve. Emerging trends include:
- AI and Automation: Cloud migration tools powered by AI can accelerate transfers and optimize workloads.
- Cloud-Native Transformation: Organizations are redesigning applications to fully utilize cloud services.
- Edge Computing Integration: Combining cloud and edge computing ensures low-latency performance for applications like IoT.
- Sustainable Cloud Practices: Optimizing workloads to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Cloud migration is now a strategic business initiative, not just an IT project. Organizations that embrace it strategically can gain a competitive edge, innovate faster, and respond to market changes more efficiently.
Conclusion
Cloud migration is a critical step for businesses seeking scalability, cost-efficiency, and digital transformation. Understanding the strategies, benefits, and challenges allows organizations to plan and execute successful migrations while minimizing risks.
By following best practices, leveraging the right tools, and preparing for post-migration optimization, businesses can maximize the value of their cloud investments. Ultimately, cloud migration is about enabling innovation, improving flexibility, and building future-ready organizations.